If you are here now, then you are one of the curious minds out there and would like to test your basic knowledge about clotting factors and anticoagulants.
Really, understanding the basics of how our blood works is crucial for good health. It can mean a lot, especially in certain unexpected situations. So, in this article, we will explore the fascinating world of clotting factors and anticoagulants.
Clotting factors are proteins in our blood that help control bleeding. When you get a cut, they work together to form a clot and stop the bleeding. But sometimes, clots can form when they shouldn’t, leading to health issues. That’s where anticoagulants come in. They are medications that help prevent these harmful clots.
But don’t worry; we will break down all of this in the following sections of this post. Whether you are a student, a healthcare professional, or just curious, this article will help you test your basic knowledge about clotting factors and anticoagulants. Just keep reading!
What’s the Coagulation Test, and What’s its Purpose?
The coagulation test is a simple blood test with a big job. It checks how well your blood clots. When you get a cut, your blood normally forms a clot to stop the bleeding. This test helps doctors understand if your blood is clotting the right way.
If it clots too slowly, you might bleed too much. If it clots too quickly, there’s a risk of blood clots in your veins or arteries. These clots can cause serious problems, like heart attacks or strokes. The coagulation test is important because it can help catch these risks early.
It’s often used before surgeries or for people taking medicines that affect blood clotting. By measuring different aspects of clotting, this test gives doctors vital information to keep you healthy.
Different Types of Coagulation Tests
Coagulation tests come in different types, each looking at a specific part of the clotting process. Each of them provides crucial information, helping doctors to tailor treatments and ensure your blood clots just right – not too quickly or slowly.
If you are looking to test your basic knowledge about clotting factors and anticoagulants, then we should talk about some common coagulation tests.
- Prothrombin Time (PT): This test measures how long it takes for your blood to clot. It’s often used to check the effectiveness of blood-thinning medications like warfarin.
- Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time (aPTT): Similar to PT, aPTT tests for clotting time. It’s especially helpful for people on heparin, another blood thinner.
- Thrombin Time (TT): TT focuses on thrombin, a key protein in clot formation. It helps diagnose bleeding disorders.
- Fibrinogen Level Test: Fibrinogen is a protein essential for blood clotting. This test measures its amount in your blood, identifying potential clotting problems.
What Are Clotting Factors?
Clotting factors are special proteins found in our blood that play a crucial role in healing wounds. When you get a cut or injury, your body’s natural response is to stop the bleeding. This is where clotting factors come into action.
They work together in a complex chain of events, like a well-coordinated team. Each factor activates the next one in the sequence, leading to the formation of a blood clot. This clot acts like a plug, sealing the injured blood vessel to stop bleeding.
Without these clotting factors, even a small wound could lead to excessive bleeding. They’re vital for our body’s ability to heal itself and prevent blood loss.
Different Clotting Factors That Are
In our body, there are several different clotting factors, each with a unique role in the blood clotting process. These factors are usually numbered using Roman numerals, from Factor I to Factor XIII.
They work in a specific order, like a domino effect, where the activation of one factor leads to the activation of the next. But just to help you test your basic knowledge about clotting factors, here is a brief overview of what these factors are.
- Factor I (Fibrinogen): This is the protein that eventually forms the clot.
- Factor II (Prothrombin): When activated, it turns into an enzyme that plays a key role in forming a blood clot.
- Factors III to XII: These include various factors like Tissue Factor (Factor III) and others like Factor VIII and Factor IX, each contributing at different stages of the clotting process.
When any of these factors are missing or not working properly, it can lead to problems with clotting. Some people might bleed too easily, while others might have an increased risk of forming clots.
How Are Coagulation Tests Performed?
Coagulation tests are simple and quick procedures, usually done in a lab or a hospital. Here’s how they are typically performed:
Preparation
First, you may be asked to fast or avoid certain medications before the test, as they can affect the results.
Blood Sample Collection
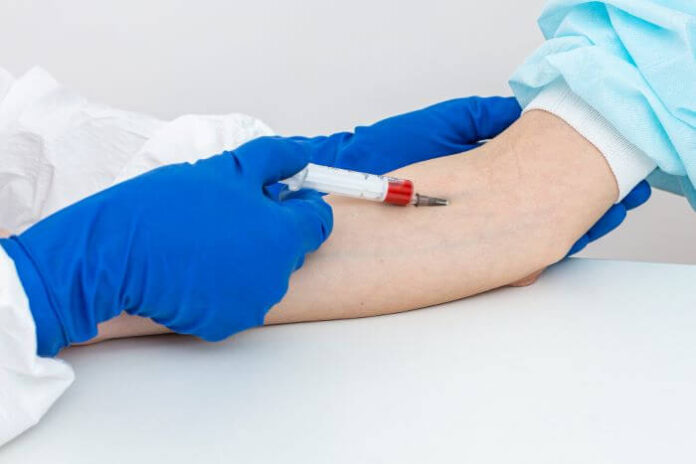
A healthcare professional will collect a blood sample from a vein in your arm. This is done using a small needle, and the process is similar to having a routine blood test. You might feel a slight pinch when the needle enters, but the process is usually quick and causes minimal discomfort.
Laboratory Analysis
The collected blood is then sent to a laboratory. There, technicians use specific chemicals and instruments to measure how long it takes for your blood to clot, and to assess the activity of various clotting factors.
Results Interpretation
The results are typically available within a few hours to a few days, depending on the test. Your doctor will interpret these results, which can tell if your blood clots normally, too quickly, or too slowly. They use this information to diagnose conditions, monitor treatment effectiveness, and manage medication dosages.
What is An Anticoagulant in Blood Tests?
This is a step further in your desire to test your basic knowledge about clotting factors and anticoagulants. We already talked about clotting factors and what they do. Now, let’s take a quick look at what anticoagulants are, too.
An anticoagulant is a substance used to prevent blood from clotting too quickly during blood tests. When a blood sample is taken, it’s natural for the blood to start clotting.
However, for many tests, especially coagulation tests, it’s important that the blood remains in a liquid state until the test is performed. This is where anticoagulants come in.
Anticoagulants work by slowing down the clotting process. They are added to the blood sample right after it’s collected. This ensures that the sample stays fluid and accurate testing can be done. Common anticoagulants used in blood test tubes include heparin, EDTA (ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid), and citrate.
However, we would like you to note that these anticoagulants are only used in the test tubes to preserve the blood sample. They are different from anticoagulant medications that some people take to prevent blood clots in their body.
What Are the 3 Stages of Blood Clotting?
#1: Vasoconstriction and Formation of the Platelet Plug
When a blood vessel is injured, it constricts (narrows) to reduce blood flow. Simultaneously, platelets (tiny blood cells) stick to the damaged site and to each other, forming a temporary ‘plug’ to stop bleeding. This is the body’s immediate response to a wound.
#2: Activation of the Clotting Cascade
This stage involves the clotting factors, which are activated in a specific sequence, like dominos. The process converts prothrombin into thrombin. Thrombin is a key enzyme that plays a central role in the clotting process.
#3: Fibrin Mesh Formation
In the final stage, thrombin converts fibrinogen (a soluble protein) into fibrin (an insoluble protein). Fibrin strands weave through the platelet plug, creating a strong and stable mesh. This mesh traps blood cells and solidifies the clot, sealing the wound and allowing the healing process to begin.
These stages work in harmony to ensure that clotting occurs quickly and efficiently, but not excessively. This balance is vital for preventing both uncontrolled bleeding and dangerous clot formation within the vessels.
Test Your Basic Knowledge About Clotting Factors And Anticoagulants – Some Terms You Should Also Be Familiar With
- Heparin
Heparin is a type of anticoagulant medication. It’s used to prevent and treat blood clots in the veins, arteries, or lungs. Heparin works by inhibiting certain clotting factors, which slows down the clotting process. It’s often given in hospitals, sometimes after surgeries or in conditions where there is a high risk of blood clots.
- Fibrinogen
As we already said, fibrinogen is a protein in the blood that’s essential for clot formation. When there is an injury, and the body needs to form a clot, fibrinogen is converted into fibrin. Fibrin forms a mesh-like structure that stabilizes the blood clot and helps stop bleeding.
- Thrombin
This is an enzyme that plays a critical role in blood clotting. It’s responsible for converting fibrinogen into fibrin during the clotting process. Thrombin also helps in activating platelets, which are crucial for the initial stages of forming a blood clot.
- Plasmin
Plasmin is an enzyme that helps break down blood clots, a process known as fibrinolysis. Once a wound has healed and a clot is no longer needed, plasmin degrades the fibrin mesh, breaking the clot apart and allowing normal blood flow to resume.
- Plasminogen
Plasminogen is the inactive form of plasmin. It circulates in the blood and is converted into active plasmin when needed. The conversion of plasminogen to plasmin is a key step in the process of breaking down blood clots.
- Streptokinase
It is a medication used to dissolve blood clots, particularly in the treatment of heart attacks and strokes. It works by activating plasminogen, which then becomes plasmin and breaks down clots. Streptokinase is often used in emergency medical situations to quickly dissolve clots and restore blood flow.
Final Note
There you have it – the intricate processes that happen when you have an injury and how your body reacts to protect your health in such a situation. If you have read to this point, then you have more than test your basic knowledge about clotting factors and anticoagulants.
You have also seen how the process of clotting works, what coagulation tests are and why they are performed, and some important proteins that are involves in the process of blood clotting. If you still have concerns or questions concerning this, please let us know in the section below. We will be glad to help!
Related Articles You Might Like: